Welcome to our fourth article in the Autoimmune Series. In previous articles, we explored various aspects of autoimmune conditions, including their development, gut health, and lifestyle management. Today, we will delve into the role of inflammation in autoimmune diseases and discuss effective strategies for managing it naturally.
Inflammation is a critical factor in autoimmune diseases, often driving the symptoms and progression of these conditions.
Understanding how inflammation works and how to manage it can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by autoimmune diseases.
Understanding Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, aimed at protecting and healing the body.
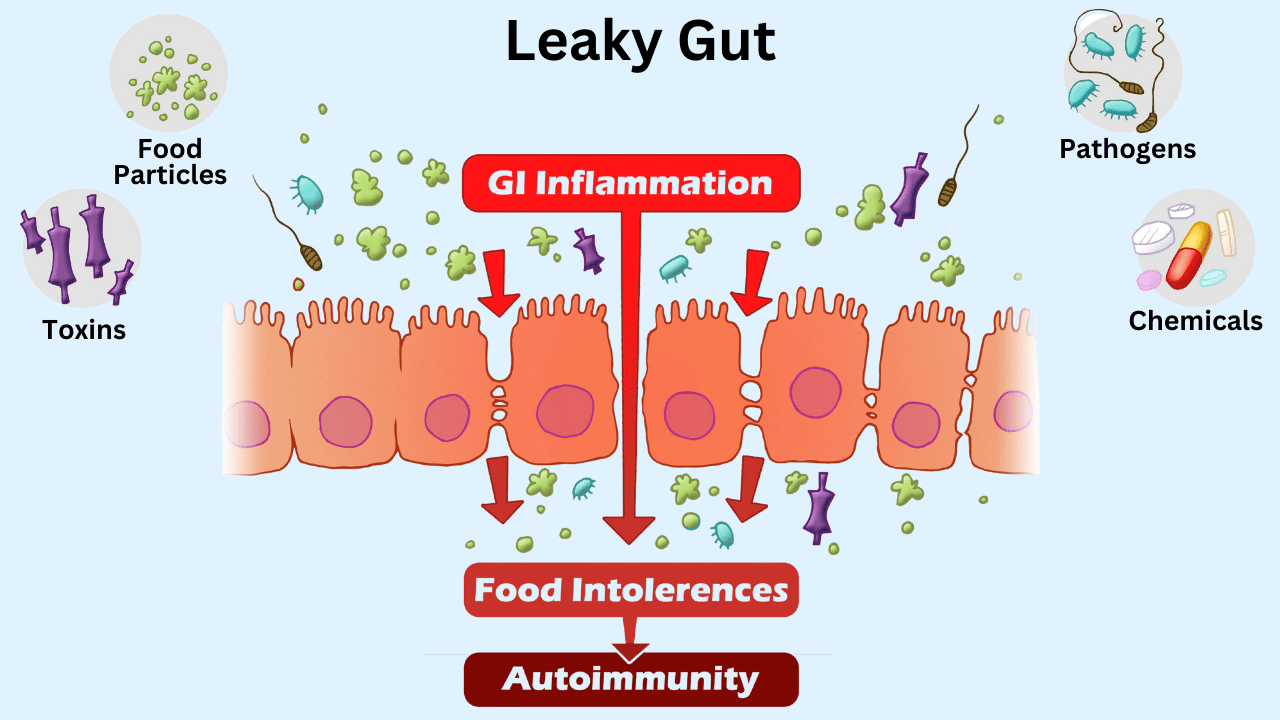
In our first blog, What Are Autoimmune Conditions & How Do They Develop?, we discuss how in autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
This persistent inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and damage to various organs and tissues, exacerbating autoimmune conditions.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet and Foods
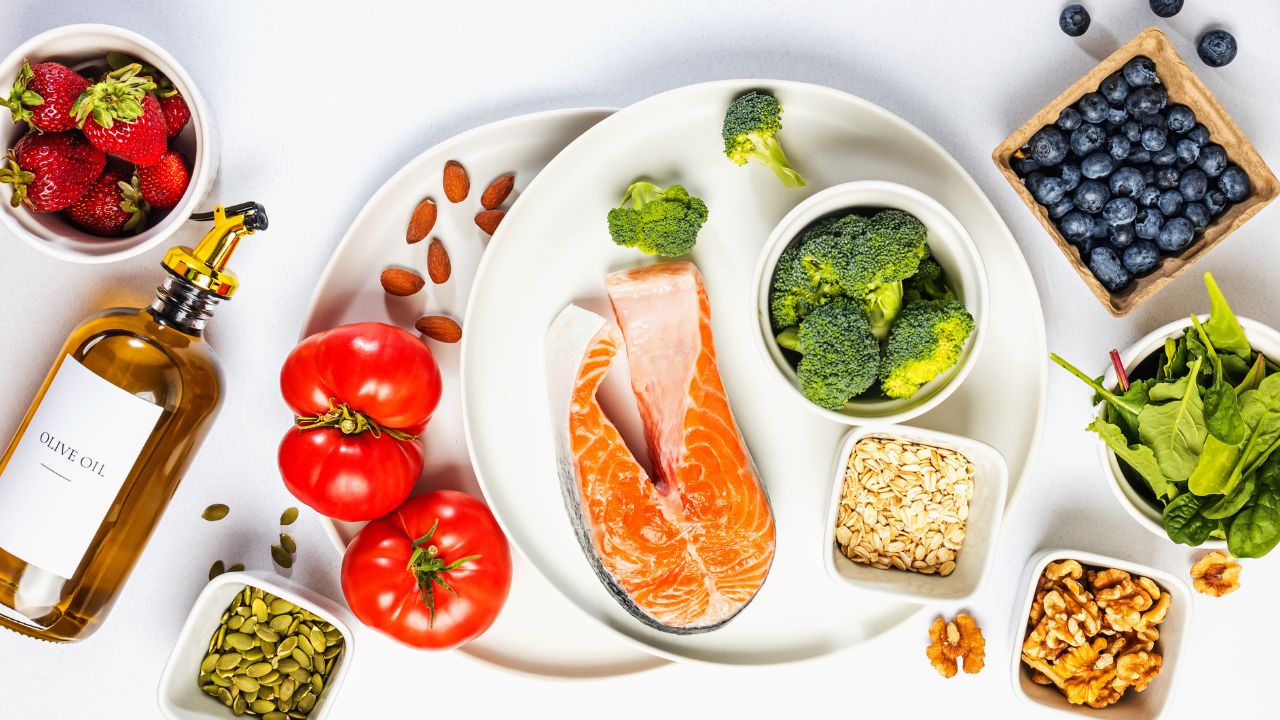
Diet plays a vital role in managing inflammation. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can help reduce inflammation and support overall health. Some key foods to include are:
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fish like salmon and mackerel can help lower inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with antioxidants.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries provide essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds offer healthy fats and fiber.
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can be added to various dishes.
Avoiding pro-inflammatory foods is equally important. Limit or eliminate processed foods, sugar, and trans fats from your diet, as these can contribute to inflammation.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Inflammation
In addition to diet, lifestyle changes can significantly impact inflammation levels.
Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, and yoga, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Stress management techniques, including meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness, can lower stress-induced inflammation.
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Inflammation
Natural remedies and supplements can also play a role in managing inflammation. Here are a few to consider:
- Omega-3 Supplements: These can help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
- Curcumin: The active ingredient in turmeric, curcumin has powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can be consumed as a tea or supplement.
- MyImmunity Supplements: Formulated with natural ingredients, MyImmunity provides essential nutrients that support immune health and reduce inflammation.
Managing inflammation is crucial for those with autoimmune diseases.
By understanding the role of inflammation and adopting strategies such as an anti-inflammatory diet, regular exercise, stress management, and natural supplements, you can better control your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
For more insights and practical tips, continue following our Autoimmune Series.
For more information on the role of diet in autoimmune health, read our previous article on The Gut-Immune Connection: How Gut Health Influences Autoimmunity.


Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.