Welcome to our third article in the Autoimmune Series. In the first article, we explored autoimmune conditions and how they develop. In the second article, we discussed strategies to balance and manage autoimmune conditions. In this article, we will delve into the critical link between gut health and autoimmune diseases, and provide practical tips for improving gut health.
The health of our gut plays a significant role in the functioning of our immune system. An imbalance in the gut can trigger or exacerbate autoimmune conditions. Understanding the gut-immune connection is essential for managing autoimmune diseases effectively.
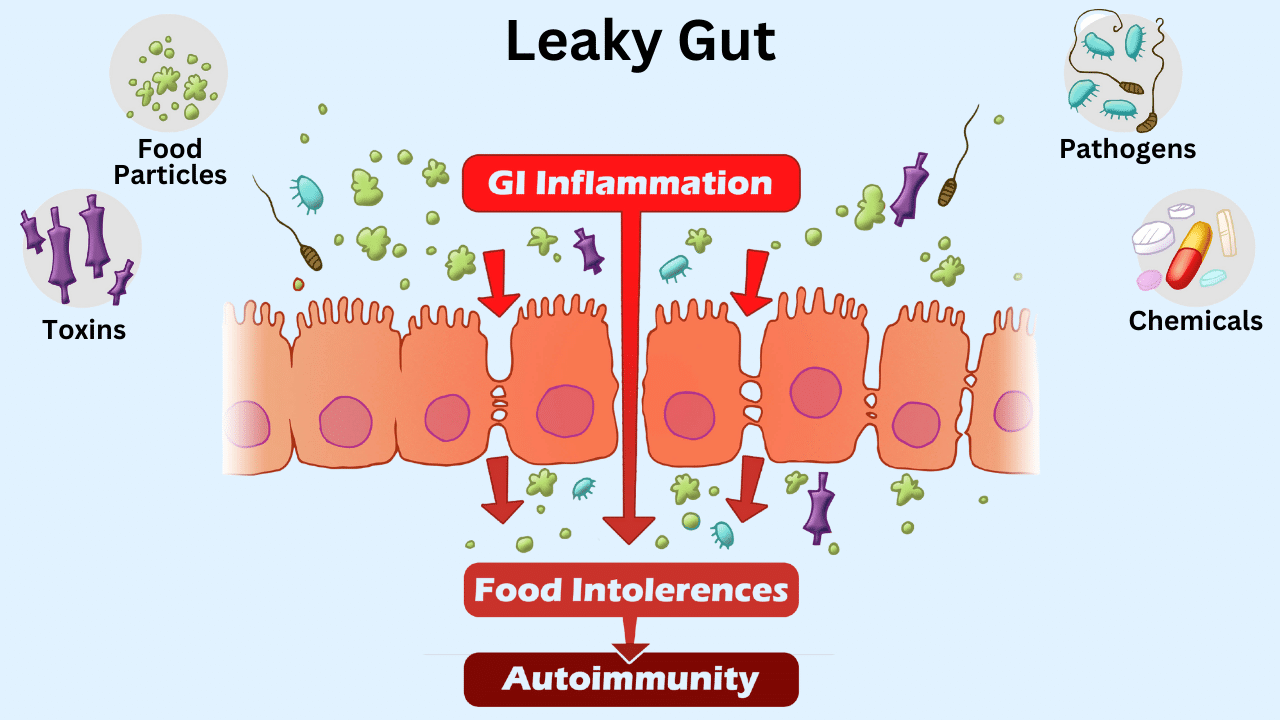
The Gut-Immune System Connection
The gut is home to a vast array of microbes that play a crucial role in immune function.
These microbes help train the immune system to distinguish between harmful invaders and the body’s own cells.
A healthy gut microbiome supports a balanced immune response, while an imbalance can lead to immune dysfunction and autoimmunity.
Importance of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
They help populate the gut with good bacteria, promoting a healthy balance.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas.
They serve as food for the beneficial bacteria, supporting their growth and activity.
Foods that Support Gut Health:
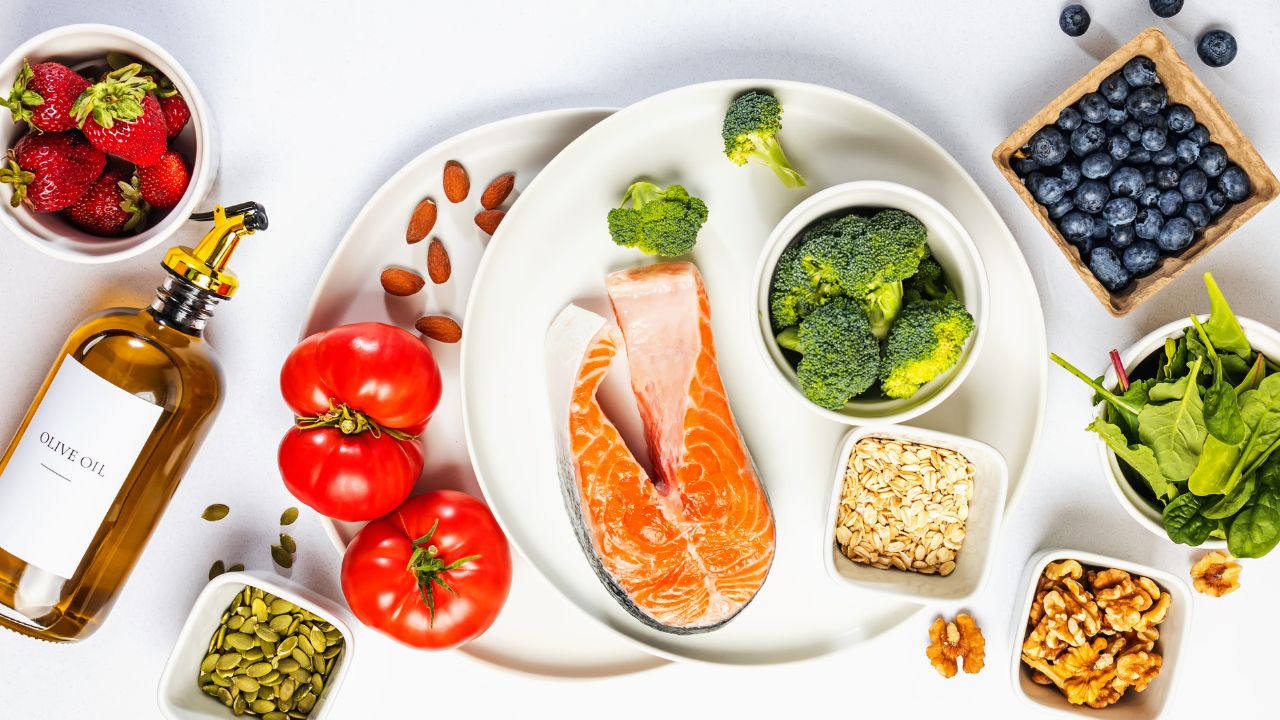
Incorporating gut-friendly foods into your diet can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
Foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, support gut health by promoting regular bowel movements and feeding beneficial bacteria.
Fermented foods like kimchi, miso, and kombucha provide natural sources of probiotics.
Additionally, foods high in polyphenols, such as berries, green tea, and dark chocolate, have been shown to promote gut health.
Lifestyle Tips for a Healthy Gut:
Maintaining a healthy gut involves more than just diet. Here are some practical lifestyle tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports digestion and overall gut health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health. Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress levels.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes healthy digestion and can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome.
- Avoid Antibiotics When Possible: Overuse of antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiome. Use them only when necessary and follow your doctor's advice.
Understanding the connection between gut health and the immune system is crucial for managing autoimmune conditions.
By incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet, eating gut-friendly foods, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, you can support your gut health and, in turn, your immune system.
For additional support, consider supplements like MyImmunity which are designed to provide essential nutrients for immune health.
Stay tuned for our next article in the Autoimmune Series, where we will continue to explore strategies for managing autoimmune conditions holistically. For more information on managing stress and its impact on autoimmune health, read our next article on Managing Autoimmune Symptoms: Practical Lifestyle Changes.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.